Extensive
involvement in products problems solving and in products
improvement from the first days of my
engineering carrier gave opportunity to evaluate hundreds
of automotive plastic assemblies with detailed
analysis of several thousand of their components. Those
were mostly complex automotive assemblies and
various mechanisms including air registers, floor consoles,
overhead consoles, center and cluster bezels,
cup-holders, sliding armrests, glove boxes, various bins,
including IP upper bins, door panels and others.
Those parts were analyzed because they caused problems
and required improvement.
Several
key observations had been made during analysis of those
multiple parts;
- about
20% of plastic products had functional and durability problems
- about 90% of the product problems were directly design
related
- similar
problems had been found on products made by different design
groups
- similar
problems were caused by the same design features imperfectly
designed
- same
design errors on different products could be improved by
the same design changes.

The
above observations initiated catalog of design errors and
their optimal design solutions. After
years
of
working with automotive plastic parts the list of the found
design errors, related problems and solutions
grew
drastically. The list included problems found during analysis
of parts benchmarked
by
different
companies
at
their tear-down centers, problems found during countless
design reviews, problems and
related
solutions described in lessons learned and best practices
by various companies as well as
issues
indicated
by tooling and manufacturing engineers working on hundreds
of plastic products.
From
the beginning of its formation the Design Errors and Solutions
list had been effectively used as:
- the
guide of recommended design details for the products development
- the
checklist for the design reviews
- the
cause and effect indicator for the product problems solving.
- a
source of information for the other documents including
DFMEA
The
analysis of plastic products had been subsequently expanded
from automotive products to products
from
other
industries
including home appliances, electronics, sport, medical products
and to toys as well,
since
some
toys
are particularly
complex
designes that must
meet tough functionality and
durability
requirements
for
a harsh
operational use conditions.
Wide
range of various analyzed products provided valuable comparison
between automotive and products
from
other industries.
Study of those products provided large collection of diverse
design solutions.
Many
of them presented
great inventiveness and quite interesting solutions for
functionality or
design
simplicity.
Analysis
of the non-automotive products
exposed similar design
errors as found on automotive
parts,
proving
that some design solutions of particular features are not
known for different design teams.
I had
developed and helped to develop tens of detailed design
guidelines for various products including
automotive
plastic mechanisms as air registers or cup-holders. I noticed
that the same or similar features
existing
on air registers or cup-holders could be found on many other
mechanisms. That is why most of
design
solutions
from various products had been added after their verification
to the Design Errors and
Solutions
catalog, creating document with a huge amount of information.
That
catalog with additional analysis of the non-automotive products,
with the design information found
on
hundreds of articles in professional magazines, with information
from plastic materials manufacturers
and
from design forums on Internet lead to the very advanced
document that had been restructured to
the
Detailed Design Guidelines and later an essence of
the Detailed Guidelines had been compressed
to the Detailed
Design Criteria & Design Checklist.
Both documents are linked to each other and their product
design body of knowledge
had been called
Both documents are linked to each other and their product
design body of knowledge had been called
KRAK for Knowledge Researched, Approved, Kept.
KRAK Design Guideline with its Design Criteria & Design
Checklist became the most versatile system
of the knowledge collected and developed for the plastic
products design. KRAK system is very effective
as the design guide for the new designs developments and
as a tool for design errors detection and
elimination at any stage of design and for evaluation
of the existing products as well.
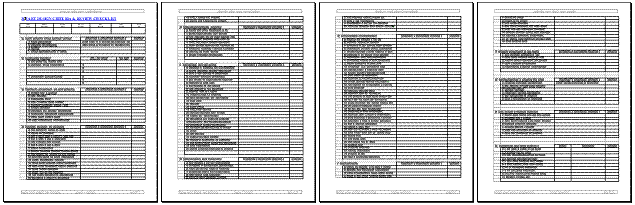
KRAK
Detailed Design Guidelines describe 14 groups of design
related areas, with 188 design features,
and
with more than
580 of their details or
subjects susceptible
for potential errors, including all those that
were
repeatedly
found on numerous plastic products as well as those observed
only few times during more
than
two
decades
of
plastic products evaluations.
That
collection of design features is accompanied by the
extensive set of the verified and recommended
design
solutions with critical details, and by advised actions
for the design errors elimination.
The
Design Checklist indicates design features, subjects and
issues recognized as the potential causes
of the
product problems
if not correctly designed and those are the following;
A -
Design inputs;
with
6 types of causes that may result in design errors and final
product problems. Some of those are:
- Studio
Concept
- Voice
of Customer
- Benchmarking
- Management preferences
B -
Part Design features (with 172 important design features
together)
- Material
selection (10 characteristics of the material related to
potential product problems)
- Design
for Tooling (23 design features and issues causing tooling
problems)
- Design
for Manufacturability (12 groups of design features that
can cause manufacturing problems)
- Design
for Assembly (32 features and issues causing potential problems)
- Design
for Operational Functions (12 features and issues for potential
errors)
- Design
for Mechanical Functionality (42 features and issues for
potential errors)
- Design
for Appearance (14 features and issues for potential errors)
- Design
for Cost Savings (6 issues to be analyzed)
- Design
for Homologations and Standards (6 groups of issues for
potential errors)
- Design
for Distribution, Installation and Service (8 features and
issues susceptible to errors)
- Design
for Recycling (7 issues to be analyzed for potential problems)
C -
CAD models quality, math data management, correctness of
engineering and G&T drawings relate
to
10 possibilities
of the product problems.
Each
of the above design features susceptible to errors has number
of small details that ought to be
developed
correctly and if any of those details is poorly designed
then problem with the product quality
or performance
may occur.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Design
Feature - Example 1:
Warp
of part is one of 12 Design for Manufacturability features
and there are several types of plastic warp.
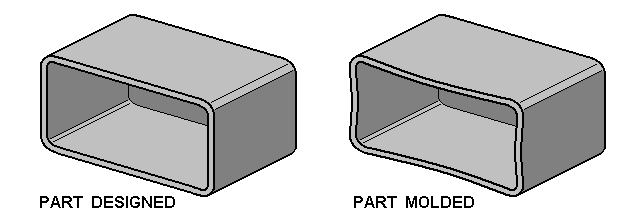
Plastic warp can be usually observed on rectangular containers
where straight by design walls become
concave after injection molding process. Warp is mostly
evident on parts made of polypropylene material
and it causes problems for assembly process, for mechanism
functioning and for the product aesthetics.
Warp of parts is produced by different speed of plastic
solidification on both sides of the wall on the part.
Delayed shrinking of the plastic at the one side of the
wall results in the part bending towards that side
of wall. Cause of the warp is related directly to temperature
difference on the IM tool surfaces.
Plastic warp can not be totally eliminated but it can be
reduced to almost insignificant dimension. There
are six practices on the part design for warp reduction
(i.e. stiffening ribs) and four practices used for
the injection mold design (i.e. water lines density and
their proper location inside the core or slide).
Additionally, warp of the part can be reduced by adjusting
parameters of the injection molding process
or with use of different plastic material as well.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Design
Feature - Example 2:
Snap
attachment is one of 32 Design for Assembly features.
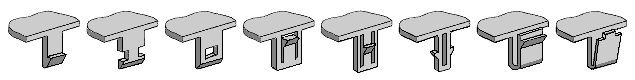
There
is a dozen types of the cantilever snaps joints (some of
them illustrated above) and several annular
types
of
snaps with tens of their variations. All those snaps have
similar functions to perform, including:
- proper
guiding to engagement position
- correct
engagement to the other retention feature
- attachment
retention under all operational forces
- multi-time
disengagements feasibility if required for service
- buzz-squeak-rattle
prevention of the attached components
The
snap feature has 8 to 12 important details depending on
the snap type and its functions. All details
of the
snap must
be designed correctly. One of those is a fillet at the base
of the snap and lack of that
fillet
may
cause breakage
of the snap during assembly process or during operational
use of the product.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Design
Feature - Example 3:
Kinematic
joint is one of 42 Design for Mechanical Functionality features.
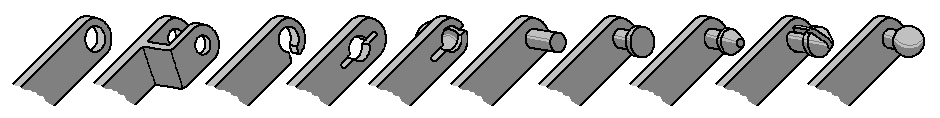
Different
types of kinematic joints and their variations are used
for mechanisms on plastic assemblies
with
linear, rotating or complex spatial movements of the elements.
Recommended
type
of a joint
depends on the following criteria:
- forces to be transferred by the joint during operational
use
- preferred method and direction of the elements attachment
- type of motion conveyed by the joint
- BSR (buzz, squeak, rattle) requirements
- materials used for both elements linked with a joint
- test forces specified for the joint retention
- number of the joint reattachments for service
Kinematic joint has 4 to 10 important details depending
on the joint type and those details relate directly
to the joint design criteria listed above. One of standard
requirements for the kinematics joint is elimination
of a rattle between connected elements and that is quite
easy to achieve with joints having elastic features.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Summary
The Detail Design Guideline described above is the very
extensive collection and classification of the
existing design engineering knowledge that applies to plastic
products and their development as the
design criteria and entirely covers all design aspects
of those plastic products.
Experience proved that integrating of the Design Guideline
and Design Checklist to the product design
and development process results in the following:
- Radically improved design quality and product quality
with a "real-time" design quality measurements
- Better optimization of the product functions and values
with more innovative design solutions
- Significantly reduced time of the product design and
development process
- Drastically shorter time of the product readiness development
for manufacturing
- Substantial reductions of tooling, manufacturing and
assembly costs
- Designer's work-load reduction with easier team leadership
and design tasks management
- Design process simplification with easier communication
between designers and project engineers
Results of Design Guidelines and Design Checklist implementation
are related mostly to the number
and precision of details examined with those documents
during the design review and to the frequency
of those reviews.
|

